The production of lithium-ion battery packs is complex due to the direct impact of safety performance on consumers’ wellbeing. High requirements for equipment precision, stability, and automation are crucial in the manufacturing process. The preparation of both positive and negative slurry requires mutual mixing, dissolution, and dispersion between liquid and solid materials, coupled with fluctuations in temperature and viscosity.
The production of electrodes serves as the basis, while electric cell production is at its core. The quality of the final product is dependent on battery assembly. The production process of lithium-ion battery packs is composed of various aspects, including positive and negative electrode pulling, steel case assembly, liquid injection and testing, and packaging.
Every stage of the production process is closely interlinked with product safety and quality. With careful management and rigid regulations, safety performance can be enhanced, ensuring the creation of top-quality lithium-ion battery pack products.
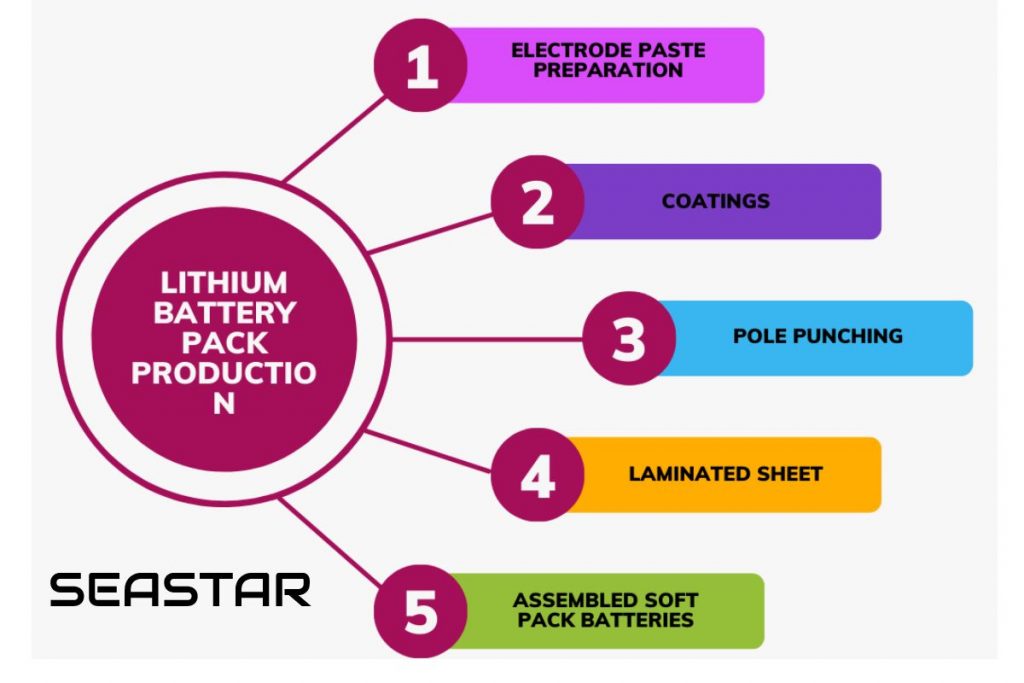
Step 1 – Electrode paste preparation
It is important that the electrode active material, binder, and solvent are mixed together and well stirred and dispersed to form a slurry. Slurry mixing (equipment used: vacuum mixer) is the mixing of positive and negative solid battery materials into a slurry by adding solvent. The slurry mixing is the starting point of the previous process and is the basis for the subsequent coating and roller pressing processes.
Step 2 – Coating
The slurry prepared in the first step is evenly coated onto the collector fluid (aluminum or copper foil etc.) at the specified thickness and the solvent is dried. Coating (equipment used: coating machine) is the process of coating the stirred slurry evenly onto the metal foil and drying it to make positive and negative electrode sheets. As the core part of the front-end process, the quality of the coating process has a profound impact on the consistency, safety, and life cycle of the finished battery, so the coating machine is the most valuable piece of equipment in the front-end process.
Step 3 – Punching
The sheets produced in the previous step are punched to the specified size and shape.
Step 4 – Stacking
Assemble the positive and negative electrode sheets and diaphragm together and finish gluing to form the core. It is the stacking of the monolithic pole pieces made in the die-cutting process into lithium-ion battery cells, which are mainly used in the production of soft-pack batteries. Compared to square and cylindrical cells, soft pack cells have obvious advantages in terms of energy density, safety, and discharge performance. However, the stacking machine is a single stacking task, involving multiple sub-processes in parallel and complex mechanism synergy, to enhance the stacking efficiency needs to deal with complex dynamics control problems; while the winding machine speed and winding efficiency are directly linked, efficiency means relatively simple. Currently, there is a gap between the production efficiency and yield of stacked cores and wound cores.
Step 5 – Assemble the soft pack battery
The cores produced in the previous step are loaded into the punched aluminum plastic film, and the top and side seals are completed (leaving an opening for liquid injection) to form an unfilled soft-pack battery.
Step 6 – Liquid injection
The specified amount of electrolyte is injected into the soft pack cell. Of course, the cells have to be baked and filled in a low-humidity environment, too much moisture is not good.
Welding machine principle
The goal of the post-production process is to complete the formation of the packaging. By the middle stage of the process, the functional structure of the lithium battery cell has been formed, the significance of the latter stage of the process is to activate it, after testing, sorting, and assembly, to form the use of safe and stable performance of the finished lithium battery. The main processes in the latter part of the process are: forming, dividing, testing, sorting, etc. The equipment involved mainly includes: charging and discharging machines, testing equipment, etc.
Formation (equipment used: charge/discharge machine) is the first charge to activate the cell, in this process, the negative electrode surface produces an effective passivation film (SEI film), in order to achieve the “initialization” of lithium batteries. Capacity Separation (equipment used: charge/discharge machine), or “capacity analysis”, is the process of charging and discharging the formed cells according to the design criteria in order to measure the capacity of the cells. The charging and discharging of the cores are carried out throughout the forming and dividing process, so the charging and discharging machine is the most commonly used core equipment in the latter part of the process. The smallest working unit of a charge/discharge machine is the “channel”, a “unit” (BOX) is made up of a number of “channels” combined, and multiple “units A “unit” (BOX) is made up of a number of “channels” and several “units” are combined together to form a charging and discharging machine.
Testing (equipment used: testing equipment) is carried out before and after charging, discharging, and resting; sorting is based on the results of the testing of the chemically formed, sub-volume battery according to certain criteria for classification and selection. The significance of the testing and sorting process is not only to exclude unqualified products but also to select cells that are close in performance to help optimize the overall performance of the battery because of the practical application of lithium-ion batteries, which are often combined in parallel and in series.
The production of lithium batteries is inseparable from lithium battery production equipment, in addition to the materials used in the battery itself, the manufacturing process and production equipment are important factors in determining the performance of the battery. In the early days, China’s lithium equipment mainly relies on imports, after several years of rapid development, China’s lithium equipment enterprises in technology, efficiency, stability and other aspects have gradually overtaken the Japanese and Korean equipment enterprises, and have the advantages of cost-effective, after-sales maintenance. At present, the domestic lithium equipment enterprise cluster has been formed, and become China’s high-end equipment business card in the international market. With the lithium leading vertical alliance and overseas expansion, lithium equipment benefit from downstream expansion ushered in a new period of rapid growth opportunities.